








Fixing Power Steering Assist Fault: A Straightforward Guide
A power steering assist fault might not feel like the end of the world, but it definitely deserves some attention. While it’s not as critical as other car issues, it’s still something that needs to be addressed ASAP. This guide breaks down how power steering works, what the problem means for vehicle control, and how to get it sorted out.
Bottom Line Up Front: Fixing Power Steering Assist Fault

In short, the fix usually involves swapping out the damaged component. It might also mean topping off the hydraulic fluid or running a full ECU diagnostic. Whatever the case, it’s best to take the car to a trusted mechanic for a check-up—driving it in this condition isn’t safe.
What Is Power Steering?
Power steering is a staple in almost every modern ride, with a few exceptions for those hardcore track cars. It’s one of those things that often goes unnoticed, but it’s doing a lot of heavy lifting behind the scenes.
Without power steering, turning the wheel would feel like trying to steer a tank—possible, but a serious workout. Power steering gives a boost by pushing the steering rack in the direction of the turn.
There are two main types of power steering systems: hydraulic and electric. The type your car has will determine what’s causing the fault.
How Hydraulic Power Steering Works
Hydraulic power steering relies on power steering fluid, which can be spotted under the hood. The cap usually has a steering wheel icon or says “Power Steering Fluid.”
The power steering pump pressurizes this fluid, directing it through a control valve. The steering rack, housed in a tubular casing with O-Rings and pressure regulators, has a piston that moves when the fluid is pumped in.
When turning the wheel, the control valve sends fluid to one side of the piston, pushing it in the opposite direction. So, turning left? The fluid goes to the left side, pushing the piston right.
How Electric Power Steering Works
Electric power steering (EPS) operates a bit differently and comes in two flavors: column-mounted and rack-mounted. The former is common in smaller cars, while the latter is usually found in trucks and SUVs.
When the wheel turns, a torque sensor measures the effort being applied. The ECU processes this info and powers the EPS motor to assist with steering. The cool part? If the motor fails, steering still works—just with a lot more effort.
And if the car has EPS, forget about hydraulic fluid or pumps. It’s all electric.
Symptoms of Power Steering Assist Fault

Spotting a power steering assist fault? Look out for these signs:
- Warning light on the dashboard
- Difficulty turning the wheel, especially at low speeds
- Car pulling to one side while driving straight
- Weird noises (like whining) when turning (for hydraulic systems)
- Visible hydraulic fluid leaks under the car (for hydraulic systems)
- Whining noise on startup (for hydraulic systems)
- Steering wheel feeling too light at high speeds (for electric systems)
- Other electrical glitches (possible ECU issues for electric systems)
What Does ‘Power Steering Assist Fault’ Mean?
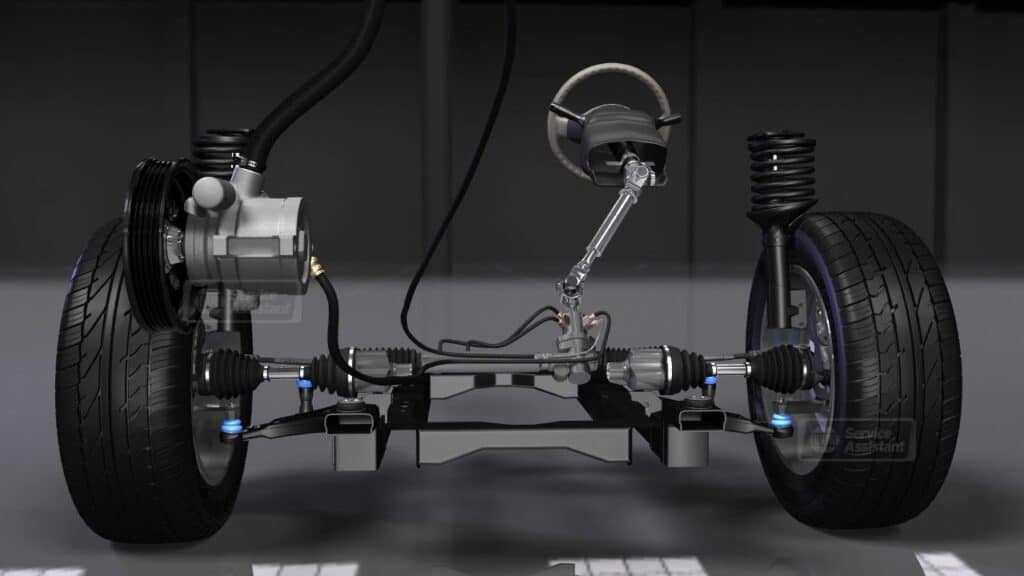

A “Power Steering Assist Fault” means there’s a hiccup in the power steering system. The issue could be with either hydraulic or electric systems, and here are some common problems:
Hydraulic Power Steering Assist Faults
- Hydraulic fluid leak
- Power steering pump failure
Less commonly, the control valve might fail if dirt gets into the fluid reservoir.
Hydraulic Fluid Leak
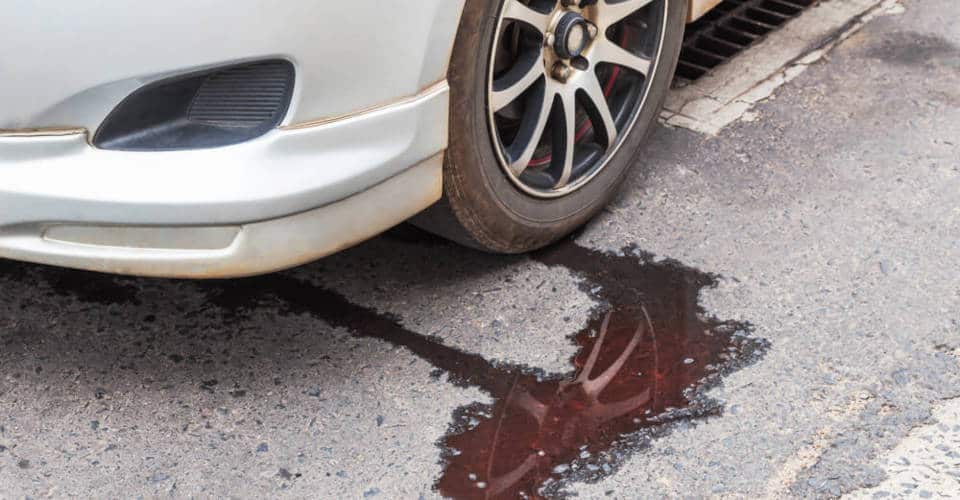

Hydraulic fluid leaks are pretty common. Often, it’s the seals around the steering rack or the pump that wear out. Look for that telltale red fluid—just don’t confuse it with brake fluid, which is a whole different level of trouble.
Power Steering Pump Failure
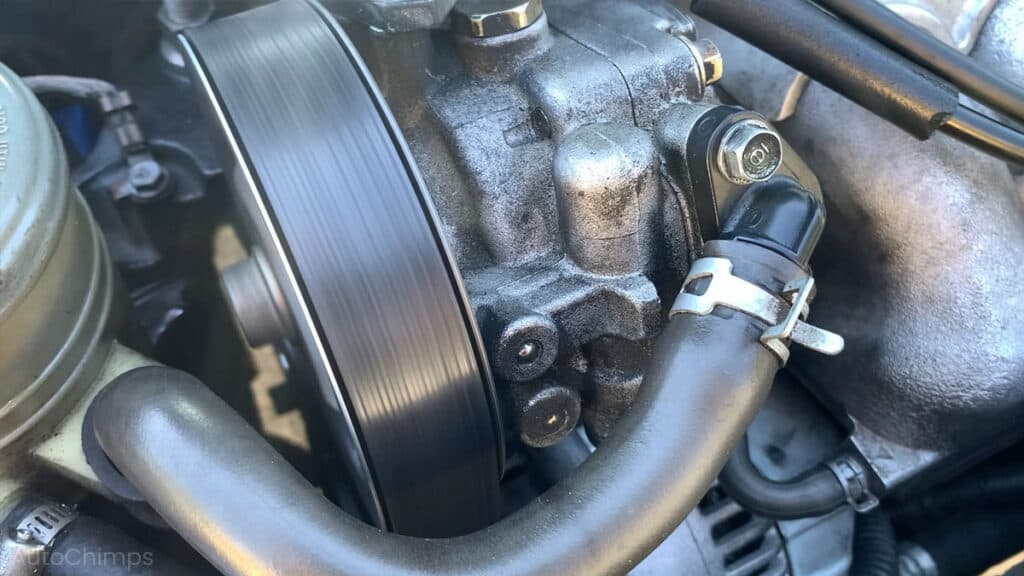

The power steering pump is driven by the engine’s serpentine belt. If it fails, there’s no pressure to assist steering. While it’s still drivable, turning the wheel will feel like a workout.
Electric Power Steering Assist Faults
In EPS systems, three main components can fail:
- Electric motor failure
- Torque sensor issues
- ECU problems
Electric Motor Failure
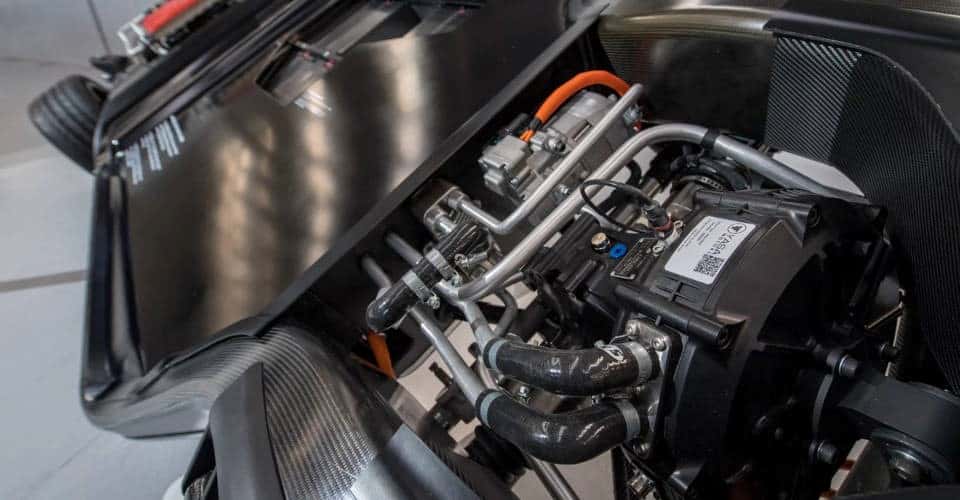

The electric motor adds torque to the steering. If it fails, steering assistance is gone. Overheating is a common culprit, especially during intense driving.
Torque Sensor Problem
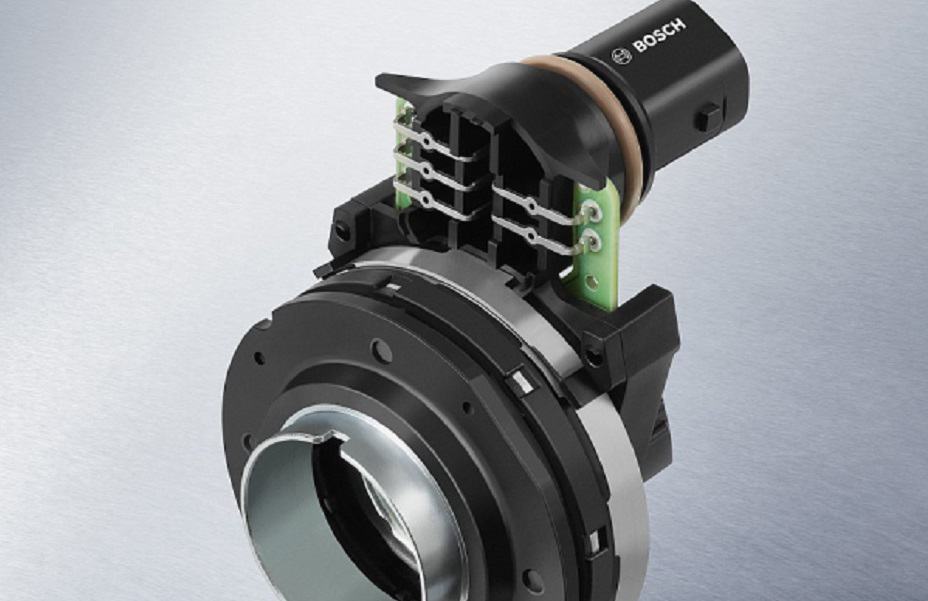

The torque sensor measures how much force is applied to the wheel. If it malfunctions, the ECU might get confused, leading to too much or too little assistance.
ECU Issue
The ECU processes data from the torque sensor. If it’s faulty, it can send incorrect signals to the motor, causing steering issues.
Is A Power Steering Assist Fault Serious?
While a power steering assist fault isn’t as dire as a blown head gasket, it still needs attention. If a warning light pops up or the steering feels off, it’s time to act.
The real danger isn’t just damage to the steering system; it’s losing control of the car. Fixing it promptly is essential for safety.
Driving with a power steering fault is possible, but it’s not ideal. If there’s any doubt, reach out to a mechanic or book a call-out service.
How To Fix Power Steering Assist Fault

Some folks wonder how to reset a power steering assist fault warning light. Sure, codes can be cleared with an OBD II reader, but if the underlying issue isn’t fixed, it’ll just come back. Best to leave that to a mechanic.
Generally, fixing the fault means replacing the faulty part. Don’t forget to check for any damage to the steering rack while at it.
Hydraulic Power Steering Fixes
For hydraulic fluid leaks, it’s usually about finding and replacing the damaged part, often new seals or components. If the pump is the issue, expect to pay around $500 to $600 for a replacement.
Electric Power Steering Fixes
If the EPS motor fails, a new one is needed, which involves some disassembly. Costs are similar to a pump replacement—around $500 to $600. The same applies if the torque sensor is the problem.
ECU issues can get pricey, often exceeding $1,000. This isn’t a DIY fix, and if the motor or sensor needs replacing, some ECU work might be necessary too.



